Next: Periodic Waveforms Up: MUMT 307: Week #8 Previous: MUMT 307: Week #8
Additive synthesis can be represented mathematically as:
![$\displaystyle y(t) = \sum_{n=1}^{N} A_{n}(t) \sin \left[\int_{0}^{t}\omega_{n}(t)dt + \phi_{n}(0)\right]
$](img1.png)
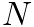 is the number of sinusoidal components,
is the number of sinusoidal components, 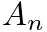 and
and  are the time-varying amplitude and frequency of the
are the time-varying amplitude and frequency of the  th sinusoidal component, respectively, and
th sinusoidal component, respectively, and  is the initial phase of the
is the initial phase of the  th sinusoidal component.
th sinusoidal component.

| ©2004-2025 McGill University. All Rights Reserved. Maintained by Gary P. Scavone. |