Next: Filters in Matlab Up: Discrete-Time Signals & Digital Filtering Previous: Steady State and Transient Response
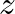 -Transform
-Transform
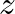 -transform is a mathematical tool that is extensively used to evaluate the properties of discrete-time systems such as digital filters. In particular, it is convenient for determining the stability of a system. It is the discrete-time equivalent of the Laplace transform, which is used for continuous-time systems.
-transform is a mathematical tool that is extensively used to evaluate the properties of discrete-time systems such as digital filters. In particular, it is convenient for determining the stability of a system. It is the discrete-time equivalent of the Laplace transform, which is used for continuous-time systems.
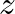 -Transform of a discrete-time signal
-Transform of a discrete-time signal ![$x[n]$](img15.png) is given by:
is given by:
![$\displaystyle X(z) \ensuremath{\stackrel{\Delta}{=}}\sum_{n = 0}^{+\infty} x[n] z^{-n},
$](img46.png)
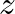 is a complex variable.
is a complex variable.
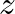 -transform maps a discrete-time signal to a function of the complex variable
-transform maps a discrete-time signal to a function of the complex variable 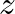 .
.
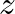 -transform is given by the Shift Theorem,
-transform is given by the Shift Theorem,
![$\displaystyle x[n - \Delta] \leftrightarrow z^{-\Delta} X(z),
$](img47.png)
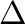 samples in the time domain corresponds to a multiplication by
samples in the time domain corresponds to a multiplication by 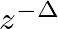 in the
in the  domain.
domain.
 -transform of a digital filter's difference equation. Given the following second-order difference equation,
-transform of a digital filter's difference equation. Given the following second-order difference equation,
![$\displaystyle y[n] = b_0 x[n] + b_1 x[n-1] + b_2 x[n-2] - a_1 y[n-1] - a_2 y[n-2],
$](img49.png)
 -transform can immediately be written (assuming the system is linear)
-transform can immediately be written (assuming the system is linear)
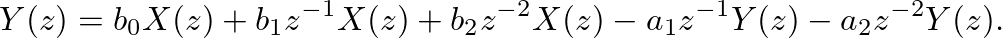
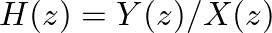 , of the filter:
, of the filter:
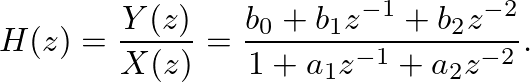
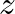 -plane, as illustrated below:
-plane, as illustrated below:
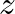 -transform is a more general version of the Discrete-Time Fourier Transform, which itself can be viewed as the limiting form of the DFT when its length
-transform is a more general version of the Discrete-Time Fourier Transform, which itself can be viewed as the limiting form of the DFT when its length 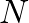 is allowed to approach infinity.
is allowed to approach infinity.
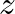 -transform by setting
-transform by setting
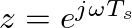 , where
, where 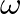 is in radians per second and
is in radians per second and 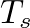 is the sample period. In the complex
is the sample period. In the complex 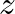 -plane, this is equivalent to evaluating the
-plane, this is equivalent to evaluating the 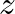 -transform on the “unit circle” defined by
-transform on the “unit circle” defined by
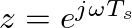 .
.

| ©2004-2024 McGill University. All Rights Reserved. Maintained by Gary P. Scavone. |