Next: Delay Line Interpolation Up: Delay Lines Previous: Tapped Delay Lines
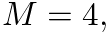 the coefficient vector would be b = [0, 0, 0, 0, 1] or more generally as b = [zeros(1, M) 1].
the coefficient vector would be b = [0, 0, 0, 0, 1] or more generally as b = [zeros(1, M) 1].

| ©2004-2025 McGill University. All Rights Reserved. Maintained by Gary P. Scavone. |