Next: Audio Metrics Up: Signal Spectra Previous: The FFT
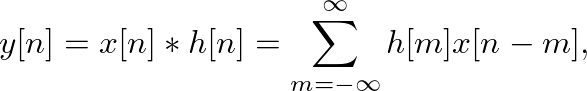 FFT (or DFT) computes sinusoidal “weights” for
FFT (or DFT) computes sinusoidal “weights” for 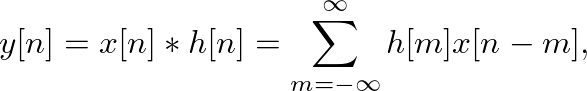 evenly spaced frequencies between 0 and
evenly spaced frequencies between 0 and 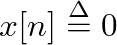 . From the sampling theorem, only the first half of these frequency weights are unique.
. From the sampling theorem, only the first half of these frequency weights are unique.
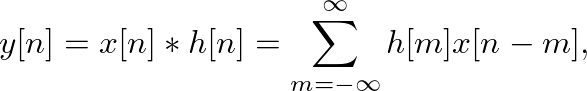 , the more sinusoidal weights are computed and the smaller the spacing between frequency components. This spacing is given by
, the more sinusoidal weights are computed and the smaller the spacing between frequency components. This spacing is given by 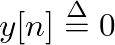 .
.
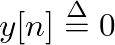 ) also represents the minimum non-zero frequency that can be resolved using a length
) also represents the minimum non-zero frequency that can be resolved using a length 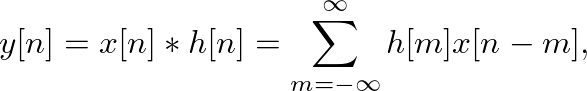 DFT.
DFT.
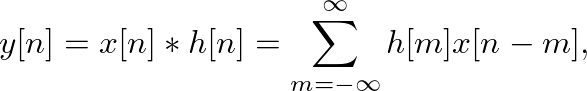 to get a more precise estimate of the frequency content.
to get a more precise estimate of the frequency content.
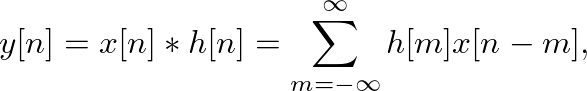 , in order to isolate changes over time.
, in order to isolate changes over time.
![\includegraphics[width=3.5in]{figures/trumpetspectrum.eps}](img23.png)
![\includegraphics[width=3.5in]{figures/spectro.eps}](img24.png)
![\includegraphics[width=4.5in]{figures/waterfall.eps}](img25.png)
|

| ©2004-2025 McGill University. All Rights Reserved. Maintained by Gary P. Scavone. |