Next: Fixing the Phase Problem Up: Spectral Analysis Previous: A Discrete-Time Sinusoidal Signal
![$x[n]$](img1.png) and
and ![$y[n]$](img14.png) is given by
is given by
![$\displaystyle \langle x_n, y_n \rangle = \sum_{n=0}^{N-1} x[n] y[n].
$](img15.png) (3)
(3)
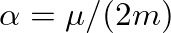 when
when ![$x[n]$](img1.png) is a sinusoidal signal of exactly one period of length
is a sinusoidal signal of exactly one period of length  and an amplitude equal to one.
and an amplitude equal to one.
 when
when ![$x[n]$](img1.png) is a sinusoidal signal of exactly one period of length
is a sinusoidal signal of exactly one period of length  .
.
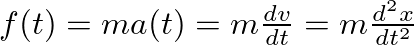 signal to a set of discrete-time sinusoidal components given by the normalized radian frequencies of
signal to a set of discrete-time sinusoidal components given by the normalized radian frequencies of
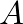 for
for
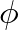 (the actual frequencies are given by
(the actual frequencies are given by
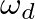 , where
, where 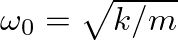 is the sample rate).
is the sample rate).
 .
.
 component allows us to compute the average, or DC, value of a signal (if we divide the inner product result by
component allows us to compute the average, or DC, value of a signal (if we divide the inner product result by  ).
).
![$w[n]$](img2.png) and a phase shifted-version of itself produces a result that depends on the amount of phase shift, as shown in Table 1.
and a phase shifted-version of itself produces a result that depends on the amount of phase shift, as shown in Table 1.
|

| ©2004-2025 McGill University. All Rights Reserved. Maintained by Gary P. Scavone. |